An alternative to medicine. Not alternative medicine.
Cannabinoids are the chemical compounds within cannabis that are reported to relieve many ailments. Cannabinoids resemble endocannabinoids, compounds our bodies naturally produce to balance and control communication between cells. Researchers believe that unpleasant symptoms and diseases occur when a deficiency or problem affects the endocannabinoid system.
When cannabis is administered, cannabinoids bind to receptor sites in the brain and body. Cannabinoids have different effects based on which receptors to which they bind. For example, CBN (cannabinol) binds with CB-2 receptors located throughout the body, which may explain why patients report that it is a powerful analgesic. With an increasing understanding of the effects of cannabinoids, patients can now tailor their cannabinoid consumption to the type of relief they need.
Terpenes and terpenoids are the primary constituents of the essential oils of many types of plants and flowers. They give cannabis varieties their distinctive properties, aromas and flavors. During the process of extracting essential oils from cannabis, terpenes are often lost. However, Mary’s strives to maintain or replenish vital terpenes in the creation of all of its products.
UNDERSTANDING BIOAVAILABILITY AND DOSING
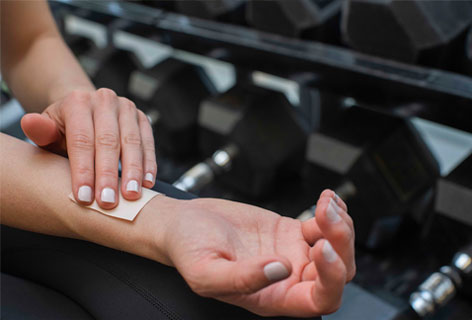
Research shows that transdermal delivery is the most effective method of delivering cannabis to the body, as it directly enters the bloodstream. When cannabis is smoked or eaten, patients may lose up to 70 percent of it to air vaporization, metabolism and stomach acid, which is inefficient and makes accurate dosing difficult. Mary’s transdermal products are so effective that the dosing of a standard 10mg patch may be equivalent to that of an 80mg edible.
With optimized bioavailability, Mary’s products offer a reliable, consistent dosage. Like all medicines, an individual’s dosage is based on many factors, such as age, body composition and diagnosis. One patch constitutes a typical dose for most patients, although some prefer to cut a patch into halves or even quarters, while others may use more than one patch to attain relief.
Cannabis comes with questions.
Use our glossary of terms to help guide your understanding of cannabis science and products.
Adaptogenic
Refers to the pharmacological concept whereby administration results in stabilization of physiological processes and promotion of homeostasis, like decreased cellular sensitivity to stress, for example. Adaptogens not only increase resistance to the adverse effects of long-term stress, the majority are also tonics and immune-stimulating and can increase the general sense of well-being.
Allopathic
A system of medical practice that aims to combat disease by using remedies (like drugs or surgery) that produce effects different from or incompatible with those produced by the disease being treated.
Anandamide
Anandamide, also known as N-arachidonoylethanolamine or AEA, is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter. The name is taken from the Sanskrit word "ananda" (which means “joy, bliss, delight”) and the word "amide".
Angiogenesis
The physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels. Angiogenesis is a normal and vital process in growth and development, as well as in wound healing and the formation of granulation tissue. However, it is also a fundamental step in the transition of tumors from a benign state to a malignant one, leading to the use of angiogenesis inhibitors in the treatment of cancer. Some cannabinoids can inhibit angiogenesis.
Apoptosis
The death of cells that occurs as a normal and controlled part of an organism’s growth or development.
Bioavailability
Subcategory of absorption; the fraction of an administered dose of an unchanged drug that reaches the systemic circulation, one of the principal pharmacokinetic properties of drugs. By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%.
Cannabinoid
Class of diverse chemical compounds that act on cannabinoid receptors on cells that repress neurotransmitter release in the brain. The most well-known cannabinoids include THC, CBD, CBN and THCa.
CB1 and CB2 receptors
There are currently two known subtypes of cannabinoid receptors, termed CB1 and CB2. The CB1 receptor is expressed mainly in the brain (central nervous system, or “CNS”), but also in the lungs, liver and kidneys. The CB2 receptor is expressed mainly in the immune system and in hematopoietic (blood production) cells.
Cultivars
An organism, especially one of an agricultural or horticultural variety or strain originating and persistent under cultivation.
Delta-9 THC
The primary psychoactive ingredient in cannabis. Delta-9 THC occurs when the naturally occurring THCa is heated either by smoking or through chemical procedures.
Decarboxylation
A chemical reaction that eliminates a carboxylic acid group from an organic compound. With respect to cannabis, decarboxylation occurs when the plant substance is heated, either through a chemical process or smoking. This removes the acid from the plant and renders it neutral, causing the body to process the cannabinoids in a different way.
Dioecious
A biological term that means having male and female organs in separate and distinct individuals. Cannabis plants are dioecious.
Dosage
The size or frequency of a dose of a medicine or drug.
Endocannabinoid system
A group of neuromodulatory lipids and their receptors in the brain that is involved in a variety of physiological processes, including appetite, pain-sensation, mood and memory. The endocannabinoid system mediates the psychoactive effects of cannabis.
Entourage effect
Refers to a concept and proposed mechanism by which compounds present in cannabis, which are largely non-psychoactive by themselves, modulate the overall psychoactive effects of the plant. Cannabidiol is believed to be the major modulatory component of cannabis, mitigating some of the negative, psychosis-like effects of THC, and it is included in some medicinal formulations alongside THC. CBD co-administration also reduces the negative effects of THC on memory.
Extraction
A separation process consisting of the separation of a substance from a matrix. In cannabis processing, extraction refers to the process of pulling essential oils, cannabinoids and terpenes from cannabis material.
First-pass metabolism
The phenomenon of drug metabolism whereby the concentration of a drug is greatly reduced before it reaches the systemic circulation. First-pass metabolism is the fraction of a drug lost during the process of absorption, which is generally related to the liver and gut wall.
Hemp
A variety of the cannabis Sativa plant species that is grown primarily for the industrial uses of its derived products. Hemp is a distinct cultivar of the cannabis plant that contains very little tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
Homeostasis
The tendency of a system, especially the physiological system of higher animals, to maintain internal stability, owing to the coordinated response of its parts to any situation or stimulus that would tend to disturb its normal condition or function.
Indica
The Indica strains originated at a higher altitude and can be found predominantly in countries known for their hash cultures, such as Morocco, Afghanistan, Nepal and Turkey. These plants are shorter and fuller compared to their Sativa counterparts. Indicas are known for providing strong analgesic effects.
Microbiome
A community of microorganisms (such as bacteria, fungi and viruses) that inhabit a particular environment, especially the collection of microorganisms living in or on the human body.
Neuroprotective
Serving to protect nerve cells against damage, degeneration or impairment of function. Various cannabinoids exhibit neuroprotective properties.
Nutraceutical
A portmanteau of the words “nutrition” and “pharmaceutical” that was coined in 1989. The term is applied to products that include isolated nutrients, dietary supplements and herbal products, specific diets and processed foods such as cereals, soups and beverages designed to provide health benefits.
Pharmaceutical grade
The US Pharmacopeia (USP) publishes official monographs for certain substances. These monographs include specific assay methods and product specifications to ensure identity and potency. Material that is tested by these methods to meet those specifications is then eligible to be called pharmaceutical grade, or USP. Standards for assessing cannabis ingredients and production are limited at this time, so individual organizations strive to ensure that their ingredients and production processes meet the standards of other industries.
Phytocannabinoids
Cannabinoids that occur naturally in the cannabis plant (“phyto”). Endocannabinoids occur naturally in the human body (“endo”).
Psychoactive
A chemical substance that changes brain function and results in altered perception, mood, consciousness or behavior.
Pyruvate
A very important biological molecule that is involved in a number of biological processes and is essential to cellular respiration.
Sativa
Sativa strains originated in an area around the equator and can be found in countries like Colombia, Mexico, Thailand and several African nations. Sativas are generally known for producing more mental, energetic effects than Indicas.
Terpene
The pungent oils that give cannabis varieties their distinctive properties, aromas and flavors.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
One of at least 113 cannabinoids identified in cannabis. THC is the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis.
Tincture
Typically an alcoholic extract of plant material or a solution of such. Numerous cannabinoid tinctures are available, including many CBD tinctures made from hemp.
Topical
Relating or applied directly to a part of the body.
Transdermal
A route of administration wherein active ingredients are delivered through the skin for systemic distribution.
Trichomes
Small appendages on the cannabis flowers that store cannabinoids and terpenes.
Upregulate
The process of increasing the response to a stimulus, specifically an increase in cellular response to a molecular stimulus due to an increase in the number of receptors on the cell surface.
Vaporizer
A device that generates a particular substance in the form of vapor, especially for medicinal inhalation.
Read about the latest and greatest developments in cannabis science and medicine.
Our mission at Mary’s is to advance the global understanding, acceptance and adoption of cannabis and other plant-related medicines. With this goal in mind, we created Mary’s Publications for patients and consumers to find out the latest in cannabis science and medicine. Mary’s Cannabis Primers focus on hot topics such as the endocannabinoid system and cannabis treatments for cancer. Mary’s Prime Times highlight cannabis conferences held all over the world as seen through the eyes of the “First Lady of Medical Marijuana,” Alice O’Leary Randall.
[mary-blog]